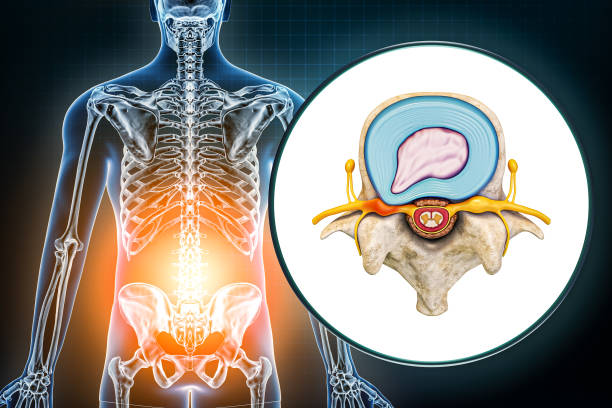
Prolapsed lumbar intervertebral disc (PLID)
Introduction Prolapsed lumbar intervertebral disc (PLID) disease, also known as a slipped or herniated disc, is a medical condition that affects the lumbar spine. The lumbar spine consists of five vertebrae, and between each vertebra lies a cushion-like structure called an intervertebral disc. When the soft inner portion of the disc protrudes through the tougher outer layer, it is referred to as a prolapsed lumbar intervertebral disc.
What is PLID disease, is important as it is a common cause of low back pain and can have a significant impact on a person’s quality of life. It is important to know the symptoms, diagnosis of lumbar, and treatment options for PLID to ensure early detection and proper management of the condition.
Et vero doloremque tempore voluptatem ratione vel aut. Deleniti sunt animi aut. Aut eos aliquam doloribus minus autem quos.
Also, Lumbosacral pain caused by a prolapsed lumbar intervertebral disc can often be treated with a lumbar discectomy.
We describe what is PLID disease, including its anatomy, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options. Additionally, the article will discuss preventive measures, coping strategies, and support groups for those living with PLID.
Anatomy of the Lumbar Spine
The lumbar spine is the lower back portion of the spine, consisting of five vertebrae labeled L1 to L5. These vertebrae are the largest in the spine, and they provide support for the upper body and protect the spinal cord.
Intervertebral discs are located between each pair of adjacent vertebrae. The discs are composed of a tough outer layer called the annulus fibrosus and a soft, gel-like inner core called the nucleus pulposus. The function of the intervertebral discs is to act as shock absorbers for the spine, allowing for movement and flexibility.
The outer fibrous ring is composed of fibrocartilage and surrounds the nucleus pulposus, holding it in place. The nucleus pulposus is composed of water, collagen, and proteoglycans, which provide it with its elasticity and compressibility. Together, the annulus fibrosus and the nucleus pulposus allow for spinal movement while providing support and stability to the spine.
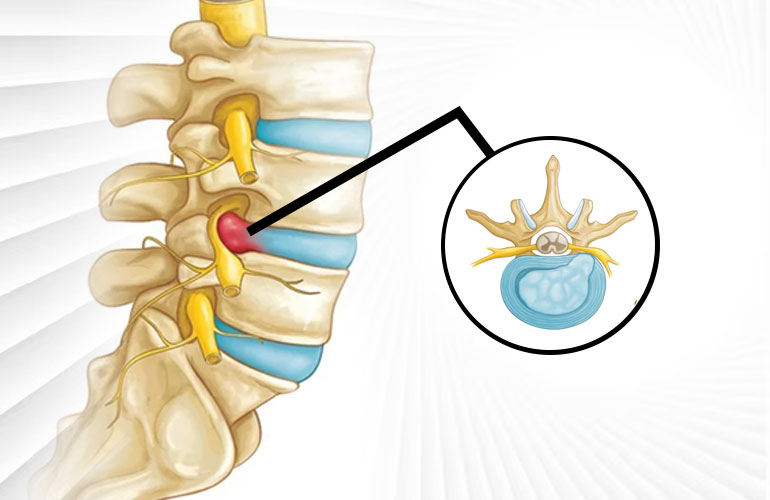
Causes and PLID Meaning
The primary cause of prolapsed lumbar intervertebral disc (PLID) is the degeneration of the lumbar disc herniation due to aging. As we age, the water content of the nucleus pulposus decreases, making it less elastic and more susceptible to injury. This can cause the disc to become brittle and prone to cracking or tearing, leading to prolapse.
Other Causes of PLID Include:
- Trauma or injury to the back, such as a fall or car accident
- Repetitive lifting or twisting motions
- Obesity or excess weight, which puts increased stress on the lumbar spine
- Poor posture or spinal alignment, which can place undue stress on the lower back and increase the risk of disc injury.
It is important to note that not everyone with these risk factors will develop PLID, and some people with no risk factors may still develop the condition. However, being aware of these risk factors can help individuals take steps to reduce the risk of future of developing PLID.
PLID Symptoms and Diagnosis
Symptoms of PLID can vary depending on the severity and location of the lumbar disc prolapsed, but they often include:
- Lower back pain
- Radiating pain down the legs, commonly referred to as sciatica/li>
- Numbness or tingling in the legs or feet
- Muscle weakness or difficulty moving the legs
- Loss of bladder or bowel control in severe cases.
Diagnosis of PLID
Diagnosis of PLID typically involves a physical exam, medical history, or clinical examination and diagnostic tests. The physical exam may include testing reflexes, checking muscle strength, and assessing sensation in the leg raise test. The medical history may include questions about the duration and severity of symptoms, history of trauma, as well as any risk factors, or previous injuries.






